Employee Health & Safety (‘EHS’) is becoming an increasingly important topic in the cannabis industry. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (‘OSHA’) is a vital agency within the United States Department of Labor. Its primary purpose is to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for employees by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education, and assistance. Unfortunately, back in 2022 there was a significant incident involving an employee's death from inhalation of ground cannabis dust at a Multistate Operator (MSO) facility. Reports, in the public domain, show OSHA investigators found the employee died from occupational asthma due to exposure to ground cannabis. One finding was that workers weren't provided enough information and training on the hazards involved in the production and grinding process. This incident illustrates the significance of both everyday hazards inside a cannabis facility as well as the responsibility of cannabis companies to prevent these incidents from occurring. In this blog, we will outline typical hazards as well as tools to assist cannabis operators in responding to OSHA inspections or similar agencies in other jurisdictions such as CCOHS (Canada) and EU-OSHA (Europe).
To give you an idea of the scope of OSHA, the org., along with its state partners, operates with approximately
1,850 inspectors responsible for the health and safety of
130 million workers across more than
8 million worksites. This ratio equates to about one compliance officer for every
70,000 workers. In fiscal year 2023, OSHA conducted a total of
34,267 federal inspections (OSHA). Within the cannabis industry, it has been observed that OSHA's involvement is likely to increase as the industry becomes more mainstream. This is particularly true in states like Colorado, where cannabis cultivation has become a significant industry. OSHA violations and fines, while not commonplace in the cannabis space, are expected to become more frequent, especially regarding issues like pesticide use in cultivation operations. To be very clear, despite the cannabis industry’s status as a federally
illegal industry, it is very much still responsible for adhering to and complying with OSHA regulations (https://mjbizdaily.com/osha-intervention-cannabis-industry-qa-jolene-donahue/).
The power of OSHA investigators ranges from fines to even stop work orders. Investigators have actual fact-finding powers under the laws and if, as an employer, you can not prove the actual facts on the ground at the time of any incident, then there is little power to mitigate the OSHA fact findings.
Cannabis cultivation and manufacturing involve a range of activities that can pose safety hazards if not properly managed. Here’s an outline of typical safety hazards and considerations in the cannabis industry:
1. Chemical Exposure
Pesticides and Fertilizers: Exposure to chemicals used in cultivation, including pesticides and fertilizers, can pose health risks. Proper handling, storage, and disposal methods are essential.
Solvents: In manufacturing processes, especially for cannabis concentrates, exposure to solvents like butane or ethanol can be hazardous.
2. Equipment and Machinery
Processing Equipment: The use of extraction machines, trimming machines, and other processing equipment can pose risks of injury. Proper training and safety equipment are necessary.
Pressurized Equipment: Equipment used in extraction processes can operate under high pressure, posing risks of explosions or leaks.
3. Electrical and Fire Hazards
High-Intensity Lighting: Grow operations often use high-intensity lighting that can increase the risk of fires and electrical hazards. This is one of the most commonly cited infractions.
Extraction Processes: Some extraction methods involve flammable solvents, increasing the risk of fires and explosions.
4. Air Quality and Ventilation
Mold and Pollen: The cultivation environment can promote the growth of mold and the spread of pollen, affecting air quality.
Volatile Organic Compounds (‘VOCs’): Solvents and other chemicals can release VOCs, requiring effective ventilation systems.
5. Physical Hazards
Ergonomic Risks: Repetitive tasks, such as trimming, can pose ergonomic risks. Ergonomic assessments and worker training can help mitigate these risks.
Slips, Trips, and Falls: Wet floors, uneven surfaces, and cluttered workspaces can lead to accidents.
6. Biological Hazards
Plant Allergens: Handling cannabis plants can expose workers to allergens that might cause reactions.
Pathogens: Cultivation environments can harbor pathogens harmful to humans.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Licensing and Inspections: Compliance with state and local regulations, including obtaining the necessary licenses and passing safety inspections, is crucial.
Worker Safety Regulations: Adherence to Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards and guidelines is mandatory.
8. Security Measures
Access Control: Due to the value of cannabis products, security measures to prevent theft and unauthorized access are necessary.
Data Security: Protection of sensitive business and customer data against breaches.
We’ve previously discussed the importance of the People Process Technology (‘PPT’) framework and that applies directly to an operator’s EHS mitigation strategies as well. Hiring people who care about safety, matters. Having properly written SOPs and a robust training program with respect to safety is critical. Leveraging technology for people to properly enforce processes & training as well as properly documenting any safety incidents is the final piece of the puzzle.
A digital EHS system –
like the one included in C15’s eQMS
- can significantly assist cannabis operators in responding to OSHA inspections by streamlining and enhancing various aspects of a safety and compliance program. Here’s how:
1. Data Organization and Accessibility
Centralized Documentation: Digital EHS systems allow companies to keep all safety and compliance documents in one place. This means that during an OSHA inspection, any requested documents, like safety training records or hazard assessments, can be easily and quickly accessed, demonstrating compliance.
Real-time Access: Inspectors may request to see records or documentation on the spot. A digital system allows for immediate access to these documents, which can facilitate smoother inspections.
2. Proactive Compliance Management
Automated Alerts and Reminders: EHS software can notify companies about upcoming deadlines for regulatory requirements, ensuring that they remain in compliance and are prepared for unannounced inspections.
Regulatory Updates: These systems often provide updates on changes in regulations, helping companies adjust their practices proactively to meet new standards.
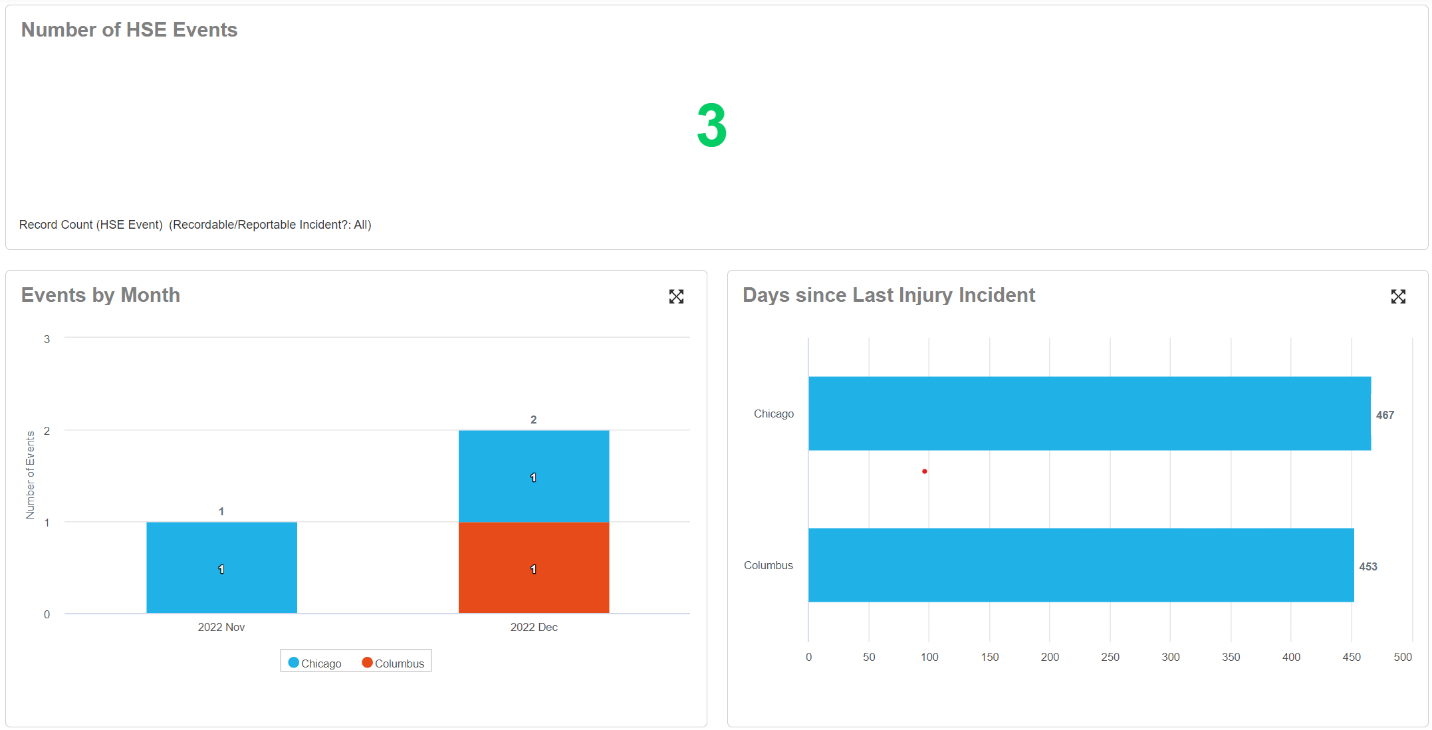
3. Incident Reporting and Analysis
Streamlined Reporting: Digital systems simplify the process of reporting incidents, near misses, and hazards, ensuring timely documentation that is essential for both internal action and regulatory compliance.
Data Analysis: They enable detailed analysis of incidents and trends, helping companies identify areas of risk and implement preventive measures, which can be highlighted during inspections to demonstrate a proactive safety culture.
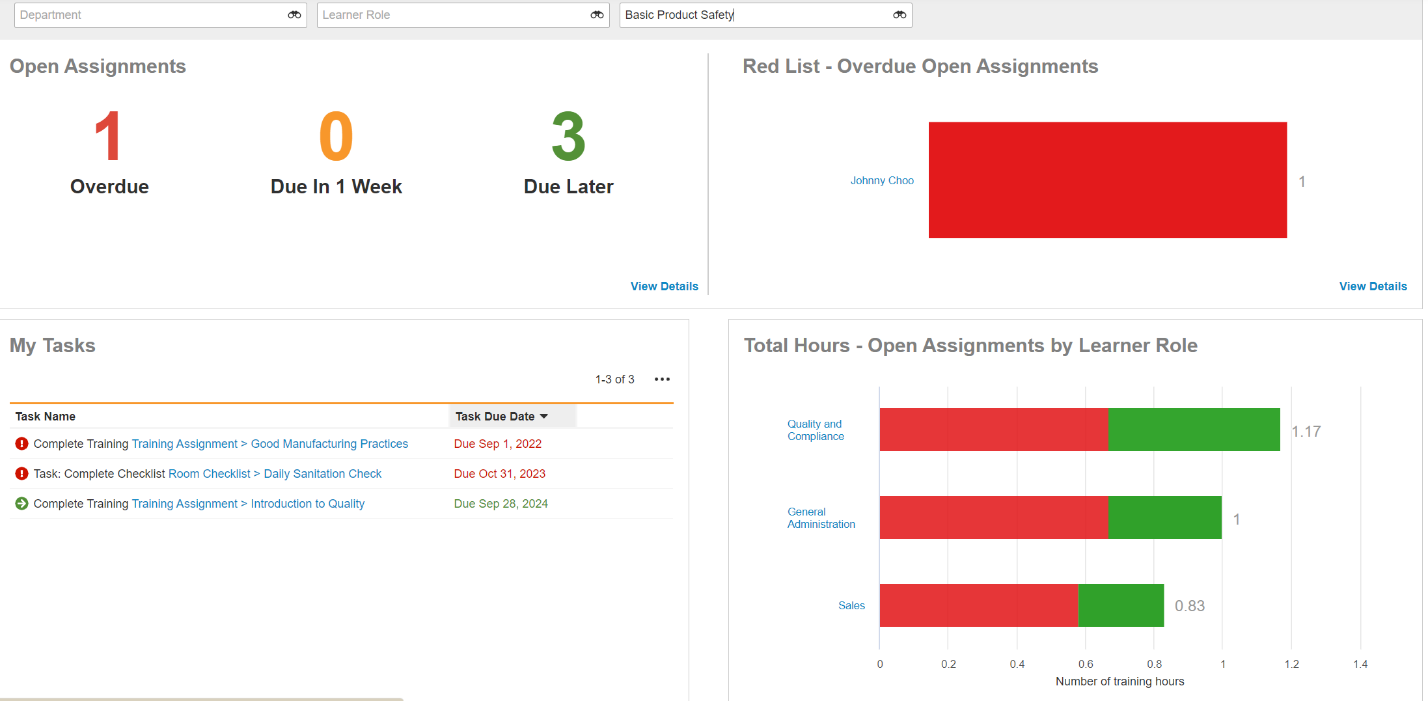
5. Training Management
Training Records: Digital EHS systems keep track of all employee safety training, including dates, topics, and scores from assessments. This information can be easily presented during an OSHA inspection to prove compliance with training requirements.
E-learning Modules: Some systems offer e-learning modules, allowing employees to complete required training efficiently, ensuring that everyone is up-to-date and reducing the risk of violations.
6. Audit and Inspection Readiness
Self-Audits: EHS software often includes tools for conducting self-audits, helping companies identify and correct issues before they become violations.
Inspection Checklists: Utilizing digital checklists aligned with OSHA standards can guide companies in maintaining compliance at all times, making real OSHA inspections less daunting.
7. Improved Communication
Stakeholder Engagement: A digital EHS platform facilitates better communication among employees, management, and external stakeholders by providing a common platform for sharing information and updates related to health and safety.
8. Documentation of Corrective Actions
Action Tracking: When issues are identified, either through internal audits or OSHA inspections, a digital EHS system can track the progress of corrective actions, documenting steps taken and timelines, which is critical information for regulatory bodies.
Implementing a digital EHS system enables cannabis companies to maintain a robust safety program, ensuring not only compliance with OSHA regulations but also a safer work environment. By leveraging technology, companies can more effectively manage their health and safety obligations, making the process of navigating OSHA inspections more efficient and less stressful.
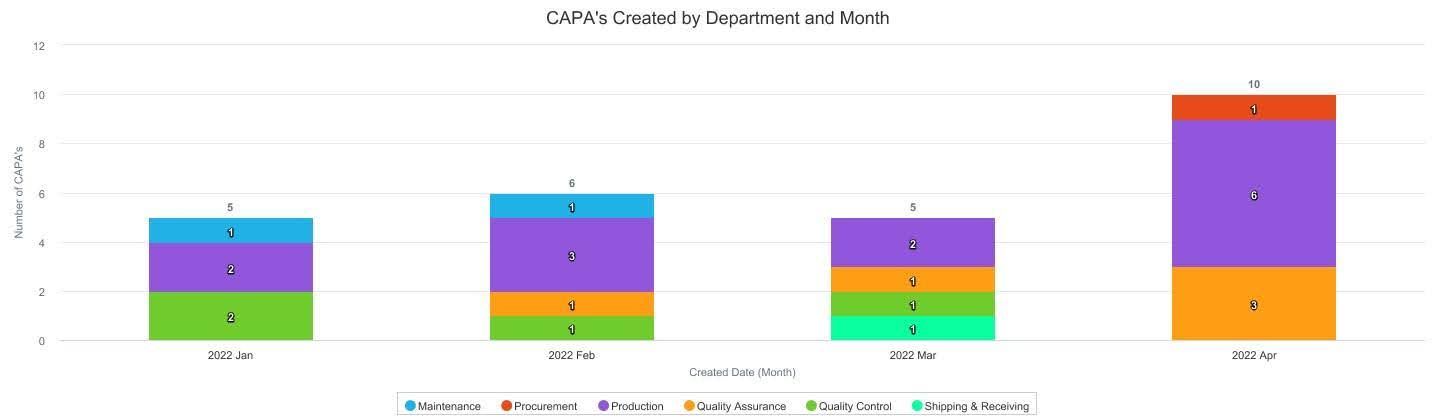
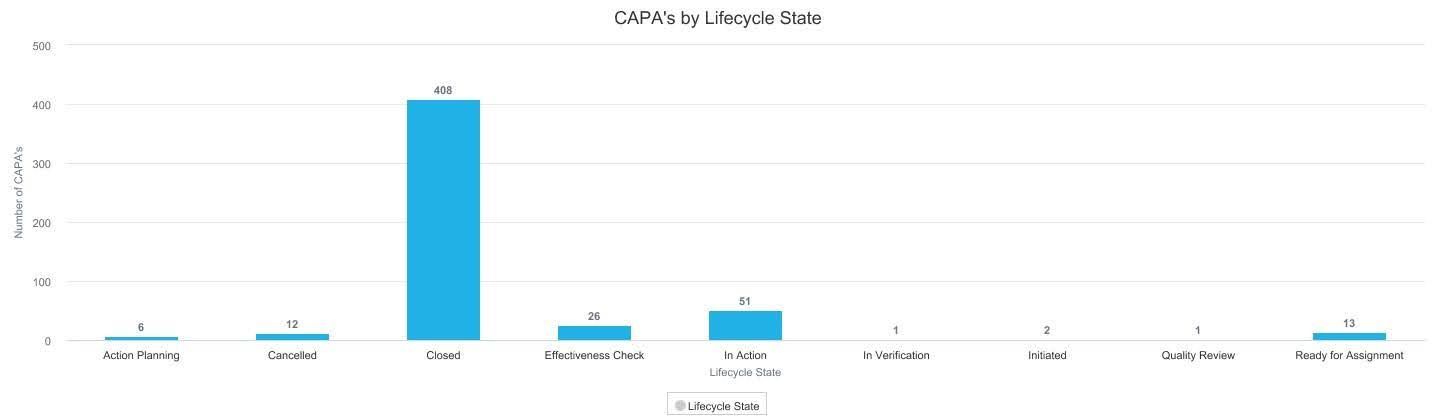

Developing and enforcing meticulous health & safety practices has now become ‘table stakes’ for the industry and failing to do so puts an operation at obvious risk for compliance violations or even worse, actual health & safety incidents. Reach out to C15 today to see how we can help https://www.c15solutions.com/demo.

